-
Free Trade Zone
What is a “Free Trade Zone”?
In the entire global economic system, the high volume of transnational transportation and circulation of products as well as production factors have reached an unprecedented scale. Various product markets have gone global. More than six hundred free trade zones across the world are becoming leading international trade circulation hubs as well as distribution and trading centers. From traditional free ports to today’s comprehensive "free trade zones" integrating commercial trade, industrial processing, and technological development, it is now the most open economic zone in the world.
"Free trade zones" hold a pivotal position in the world economy and trade, and multinational companies make extensive use of "free trade zones" to strengthen their global production network and internal trade.
-
Free Trade Zone
Why does Taiwan need to establish “Free Trade Zones”?
To make use of the world’s resources, talent, and favorable economic environment, and promptly deliver the products to customers, thereby quickly satisfying consumers’ diversified and personalized product requirements, product suppliers adopt the global logistics management model by linking up the entire supply chain, including obtaining raw materials, production, shipment, and even marketing. “Free Trade Zone” has become a normal mode of operation for multinational companies.
To seize the opportunity brought about by such a business model, governments around the world have been vigorously promoting various types of free trade zone projects in recent years. The world already has more than six hundred free trade zones of different types, and the number has been rapidly increasing in the past two years. Take the Asian region for example; besides the rapidly expanding free trade zones of Singapore and Hong Kong which we are familiar with, Japan and South Korea have also been promoting free trade zones in recent years, and even China is also establishing free trade zones successively. Hence, if Taiwan does not promote free trade zones, it could be marginalized in the global supply system.
Another unique reason for Taiwan to promote free trade zones is that Taiwanese businessmen have been investing heavily in South East Asia, China, and even Eastern Europe in recent years. Quoting the figures mentioned by former vice minister Shih of the Ministry of Economic Affairs in “Challenge 2008-National Key Construction Project Seminar”, Taiwanese businessmen have created more than 20 million job opportunities with their investments abroad far exceeding USD100 billion. With such huge overseas investment, if the products manufactured there can use Taiwan as a gateway, with transshipment and assembly through Taiwan, or perform other value-added activities, it’s conceivable that it would drive the domestic economy. Hence, establishing free trade zones to simplify the various procedures such as transshipment and customs clearance for shipping back the goods for value-added activities, and shipment to the places around the world, so as to increase the willingness of Taiwanese businessmen and multinational companies to use Taiwan as an important base for their global logistics, will be a key factor in determining whether Taiwan’s economy will hit another peak.
In view of this opportunity, the Council for Economic Planning and Development (CEPD), based on the resolution by the National Development Council on the feasibility of establishing a free trade zone, treats the planning of a free trade zone as the main factor in driving the next phase of the global logistics project. A preliminary plan was drafted and submitted to the Executive Yuan’s Finance and Economic Committee for resolution, and the CEPD then gathered the relevant agencies for conducting detailed planning.
-
Free Trade Zone
What are the characteristics of Taiwan’s Free Trade Zone?
Free Trade Zones provide enterprises with excellent geographical location advantages and highly efficient deep processing capabilities. Taiwan can be an important link in the global supply chain for cargo owners, where they can fully utilize Taiwan’s world-class manufacturing, processing and research and development capabilities. In addition, according to the “Act for the Establishment and Management of Free Trade Zones” established by the Council for Economic Planning and Development (CEPD), a Free Trade Zone is to be equipped with the following characteristics:
1. The design concept of “Within national territory but outside customs jurisdiction”: a Free Trade Zone is designed based on the concept of “within national territory but outside customs jurisdiction”. Businesses within the zone can enjoy highly efficient logistics services, and goods within the zone can circulate freely, without restrictions by the levels of declarations for circulation between bonded warehouses.
2. Autonomous management of free-trade-zone enterprises: The management of enterprises in the free trade zone will adopt a highly autonomous management system in place of a government management system, reducing actual involvement by the government, so as to facilitate the smooth flow of goods and manpower in the free trade zone, thereby increasing the enterprises’ willingness to enter.
3. Tax exemption for goods and equipment within the zone: Overseas goods and self-use equipment transported into a free trade zone by a free-trade-zone enterprise for its operations shall be exempted from tax (exempted from customs duty, commodity tax, business tax, tobacco and wine tax, tobacco health and welfare surcharge, trade promotion service fee, and commercial port dues).
4. Free circulation of goods: Entry or storage of goods (including China products) from overseas or other domestic free trade zones, or shipping of free-trade-zone goods to overseas or other free trade zones, may be carried out upon reporting to the customs according to the standard format or in writing, and receiving an electronic reply from the customs of completion of the record.
5. In-depth value-adding of goods: Free trade zones engaging in more in-depth processing such as component assembly will give full play to the advantages of Taiwan in the manufacturing of high value-added products, thus strengthening our global logistics competitiveness.
6. Bring in business activities
A. To facilitate foreign business personnel entering the free trade zone to conduct business activities, relevant competent authorities will be coordinated to flexibly relax the entry visa application procedures for international business personnel (including China) under the existing legal system.
B. A Free trade zone provides exhibition and trade activities functions.
7. For work conditions, the employment ratio of foreign workers can be flexibly relaxed: The number of domestic employees employed by a free-trade-zone enterprise shall not be lower than 60% of its total employees.
8. Boost fund circulation
A. It may engage in foreign currency exchange and remittance, and foreign currency transactions: An offshore banking unit may handle business related to the letter of credit in foreign currency, advice, negotiation, import and export collection, foreign currency exchange and remittance, and foreign currency transactions of the free-trade-zone enterprises.
B. It may establish a holding company specializing in offshore investment: A foreigner may apply to the management authority for the establishment of a holding company specializing in offshore investment.
9. One stop administrative service: As far as possible, the free trade zone’s management authority shall be authorized to handle administrative management and supplementary administrative matters within the zone. If direct authorization is not possible due to the restrictions of other laws and regulations, the management authority of the free trade zone shall take charge after being mandated or commissioned by the competent government authority in charge of the relevant end-enterprise(s). If the matter is still not possible to be mandated or commissioned, the competent government authority in charge of the relevant end-enterprise(s) shall set up an office in the free trade zone to handle the matter so as to increase administrative efficiency, and attain the efficacy of single-stop service.
-
Free Trade Zone
What are the specific contents of the “Free Trade Zone”?
1. Background
A. Change in the overall circumstance: (a) China and Taiwan have successively joined the World Trade Organization. In the future, the new cross-strait economic and trade relationship should develop gradually and slowly under the WTO framework. (b) The business sector actively develops the “global logistics management” business model: Enterprises are establishing globally, linking every process from material preparation, production, shipment, and customs clearance, to market distribution, to fully achieve Just-In-Time management.
B. Cross-strait policy (a) Caution and self-restraint: The “caution and self-restraint” policy restricting Taiwanese businessmen from investing in China has been significantly relaxed to “proactive liberalization with effective management”. (b) The function and scope of offshore shipping centers have been gradually expanded: The function and scope of offshore shipping centers have gradually expanded, breaking the taboo of direct cross-strait shipping.
C. Free ports and free trade zones drive international trade circulation: Over 600 free trade zones in the world have become the world’s most open economic zones, hub, distribution, and trading centers that drive international trade circulation.
2. Questions and description
A. Objective (a) Extending the current results of the global logistics development project, continuing to promote liberalization and internationalization of work. (b) Embracing the challenges from neighboring Asia Pacific countries actively establishing free trade zones. (c) Breaking through the current limits of bonded warehouse and engagement in high value-added processing; promoting the trade development of re-export, as well as processing and re-export. (d) Raising operational efficiency of the relevant scope of port and airport.
B. Significance (a) By setting up a control area, complete autonomous management will be adopted if goods within the zone do not enter the local market. (b) Goods may engage in storage, transshipment, value-adding process, etc., under highly autonomous management systems.
C. Positioning as a “free trade zone” can provide comprehensive discounts and simplify custom procedures, enjoy highly efficient logistics services, and bring in international business personnel to engage in business activities. In the midst of developing a global logistics center in the country, it can be the main focus in the next phase of the global logistics development project.
D. In terms of sites selection, Taoyuan Air Cargo Park and Kaohsiung Air Cargo Park which are being actively promoted, and other airports, regions neighboring ports or other regions that may make use of technological escort and are equipped with segregation facilities, as long as its scale and system comply with the requirements, can consider adopting "Free Trade Zone" business mode to increase operational efficiency and competitiveness.
-
Free Trade Zone
Why does the establishment of a “Free Trade Zone” need to be regulated by special law?
The operation of the “Free Trade Zone” is complex, involving matters such as customs, taxation, personnel movement, etc. If it is done by only amending relevant laws and regulations, it is easily subject to the restrictions of various laws, and unable to consider the needs of a “free trade zone” as a whole. By establishing special legislation, it can have the overall coordination effect. In addition, with special legislation or special laws, it can increase legislative efficiency and facilitate future amendments.
-
Free Trade Zone
Is a free trade zone an abstract concept or physical structure?
1. In terms of abstract concept, the free trade zone represents a special area of "within and outside the customs". The biggest difference between the current processing export zone and science park is that the customs clearance procedures for goods and personnel are greatly simplified.
2. However, the free trade zone is not only an abstract change, it also includes the construction of information technology, such as the cargo condition tracking system and the operation of deep processing, exhibition, foreign exchange business and other businesses in the area. Therefore, the free trade zone can be said to have both concept updating and physical construction.
3. In the future, processing export zones and science parks can apply to be set up as free trade zones in accordance with the “Regulations on the Management of Free Trade Port Zones”, and carry out deep processing, manufacturing, warehousing and logistics, trade or exhibitions and other activities in the zone.
-
Laws & Regulations
Relevant laws and regulations of Taoyuan Aviation Free Trade Zone
-
Laws & Regulations
Farglory Free Trade Zone Management Convention
-
Charges & Rates
Charges & Rates
-
Dangerous goods
Definition of Dangerous Goods
Dangerous goods are substances and articles that pose a hazard to health, safety, property and environment, or substances and articles on the list of dangerous goods according to the air transport regulations, or substances and articles classified as dangerous goods according to the air transport regulations.
-
Dangerous goods
Classification of Dangerous Goods
-
Dangerous goods
Responsibilities of cargo owner and shipper
Cargo owners shall deliver dangerous goods to the airline company according to the Dangerous Goods Regulations set by the International Air Transport Association (IATA). In addition, the owner needs to comply with the regulations applicable to the cargo transportation, transit and destination country.
Cargo owners are required to guarantee that the substances or articles to be transported are not prohibited items for air transportation.
Cargo owners are required to properly identify, classify, package, mark and label the substances and articles to be shipped, and prepare the necessary documents according to the “Dangerous Goods Regulations”.
-
Dangerous goods
Hidden Dangerous Goods
Goods declared under general product name may also contain hazardous articles that are not apparent. When it is suspected that the cargo may contain dangerous goods, the cargo acceptance personnel shall seek confirmation from the shipper or its agent that each piece of goods they consign does not contain dangerous substances. When consigning goods containing the following items, the shipper shall check the items it consigns in accordance with the classification and definition of dangerous items in the “Dangerous Goods Regulations” and need to specify that “the goods in the cargo are not dangerous” on the “Air Waybill”.
-
Dangerous goods
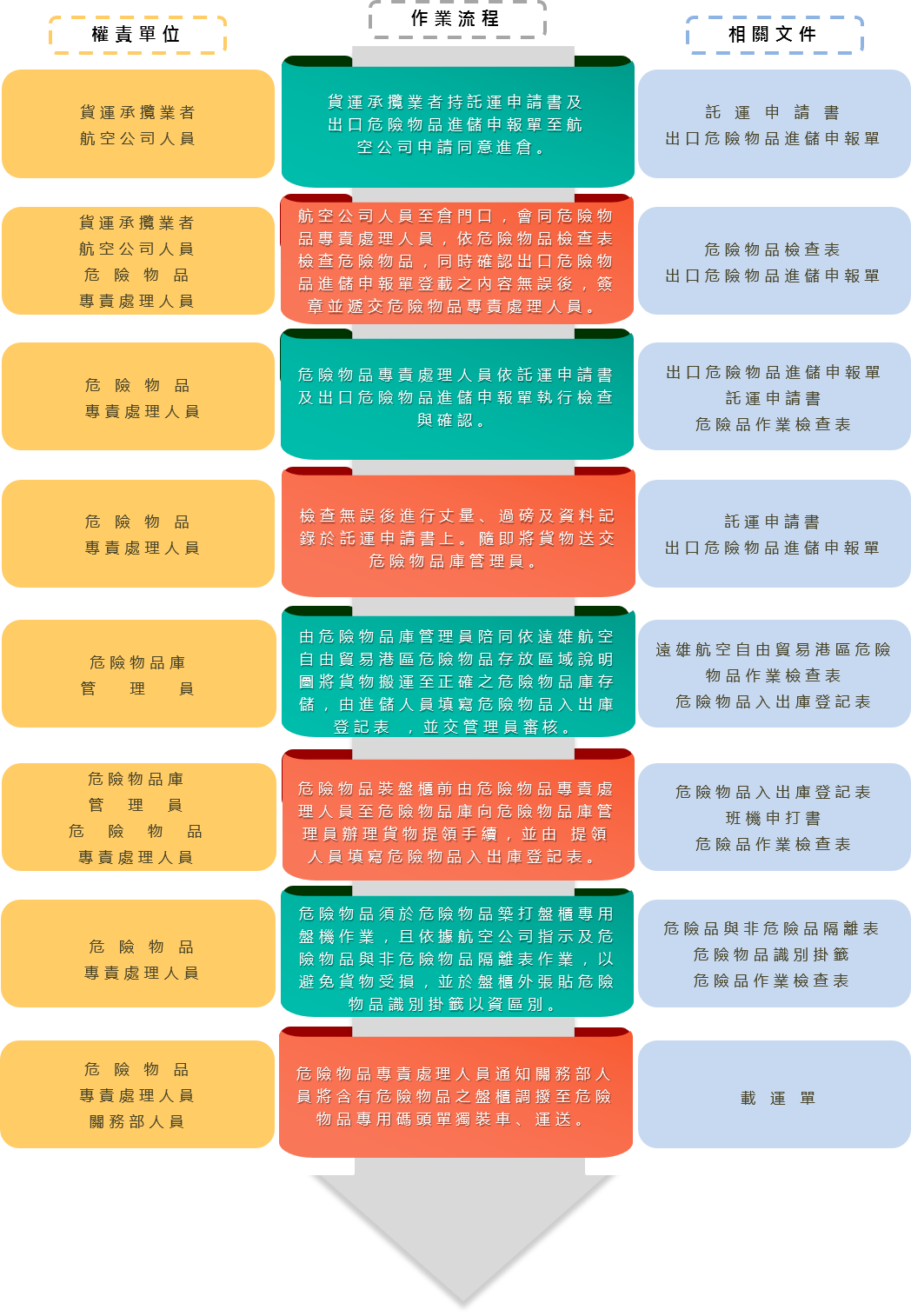
Operation Process of Export Dangerous Goods
-
Dangerous goods
Procedures for exporting dangerous goods
(1) Acceptance and checking
1. Before the dangerous goods enter the warehouse, the airline personnel shall be present at the warehouse gate, and according to IATA DGR’s transportation regulations of dangerous goods and the company’s policy of accepting dangerous goods, inspect dangerous goods against “Dangerous Goods Checklist” (Attachment I, II), and check whether the declarations in the “Shipper’s Declaration For Dangerous Goods” (Attachment III) and “Dangerous Goods Acceptance Form” (Attachment IV) are according to the regulations of IATA DGR. After completing the check, the airline personnel shall affix the airline company’s stamp and signature on the declaration form, and hand them to the personnel in charge of handling dangerous goods.
Remarks:
A. Warehouse Gate 27 of the Company’s export warehouse is the dedicated gate for accepting dangerous goods.
B. The airline company shall inspect the dangerous goods at the warehouse gate together with the dangerous goods handling personnel.
2. The freight forwarder shall submit the “Dangerous Goods Acceptance Form” and “Consignment Application Form” to the dangerous goods handling personnel to conduct acceptance of dangerous goods. After receiving the above documents, the dangerous goods handling personnel shall carry out the following pre-acceptance inspection:
A. Check whether the outer packaging is damaged or leaking, and if such conditions exist, request the freight forwarder to take it back and repack.
B. Whether or not various types of incompatible dangerous goods, including dangerous goods with multiple hazards, are placed in isolation, and whether or not the goods are neatly stacked in the direction indicated by the arrow.
C. Check whether the content of the “Dangerous Goods Acceptance Form” are duly filled in (for example, specifying the explosives, ignition point of flammable liquids, etc.), and whether the airline company has affixed a stamp and signature.
D. Whether the dangerous goods label and packaging mark of the goods checked conform with the contents declared in the “Dangerous Goods Acceptance Form”. If the label and mark of the dangerous goods do not match the declaration, the freight forwarder shall check and amend, and then request the airline company to inspect together, before moving the goods to the warehouse upon confirmation.
E. After inspection, measure and weigh the goods, record the results in the “Consignment Application Form” and affix with “Dangerous Goods” stamp, return the dangerous goods to the freight forwarder to be delivered to the dangerous goods warehouse and inform the warehouse administrator. Accompanied by the administrator, the goods shall then be moved to the correct dangerous goods warehouse for storage according to “Farglory Free Trade Zone Dangerous Goods Storage Area Diagram” (Attachment VI), and the “Dangerous Goods Entry and Exit Form” (Attachment VII) has to be filled in and submitted to the dangerous goods warehouse administrator for review.
F. If the general receiver, when receiving goods at the warehouse gate, encounters liquid chemical materials in barrels or goods emitting a strange smell but with no dangerous goods label affixed, shall inquire the cargo owner and notify the airline personnel and dangerous goods handling personnel to confirm on site if the item is dangerous goods. If it is confirmed that the goods are dangerous goods, the freight forwarder has to handle them according to the warehouse entry procedures.
G. If the general receiver, when receiving goods at the warehouse gate, encounters goods affixed with dangerous goods label but are undeclared goods, shall inquire the cargo owner and notify the airline personnel to confirm on site if the item is dangerous goods, and shall not remove the dangerous goods label by themselves.
H. To prevent the dangerous goods from falling and posing danger when transported in the warehouse, stack the goods as neatly and stably as possible, with the dangerous goods label facing outwards, and the total height shall not exceed the height of the cargo basket.
(2) Goods Storage Operation
1. The goods receiving personnel, together with the dangerous goods warehouse administrator, shall stow the measured and weighed dangerous goods in the allocated space according to “Farglory Free Trade Zone Dangerous Goods Storage Area Diagram”.
2. When entering the warehouse, fill in “Dangerous Goods Entry and Exit Form”. The warehouse’s dangerous goods storage area has been designated according to “Dangerous Goods Storage Segregation Table” (Attachment VIII), and the goods receiving personnel need to stow the goods in the warehouse according to the instruction on the tag. The dangerous goods warehouse administrator needs to check the documents and ensure the goods are stowed in the correct place. The following shall also be complied:
A. When stowing dangerous goods with multiple hazards, its primary hazard shall be the basis of classification of storage. If the dangerous goods have sub-hazards, they must also comply with IATA DGR Table 9.3.A according to the sub-hazards, and necessary segregation measures shall be taken for incompatible dangerous goods in the warehouse storage area.
B. When storing Class 4.1 and Class 5.2 dangerous goods, place the goods in a ventilated area, prevent contact with heat source or under direct sunlight, and affix with “Keep Away From Heat” label.
C. When storing radioactive material of II-yellow or III-yellow packaging or overpack and its content contains fissile material, the transport index of a single good cannot exceed 50 (TI<50) and the goods shall be kept at least 6 meters apart.
(3) Goods Picking Operation
For palletization of dangerous goods, the dangerous goods handling personnel shall provide the dangerous goods warehouse administrator at the dangerous goods warehouse with the flight palletization form for picking procedures. After filling in the “Dangerous Goods Entry and Exit Form”, the dangerous goods handling personnel can then move the goods to the export operation area. However, the goods shall be moved carefully and slowly and appropriate preventive measures shall be taken to avoid causing damage.
(4) Palletization
1. Palletizing of dangerous goods shall be carried out at the palletizing machine dedicated for dangerous goods (palletizing machine No. 6).
2. During palletizing, if suspected dangerous goods are found and not specified in the palletizing plan, report to the Customer Service Section and officer on duty at the Operations Section immediately, and contact the airline company to ascertain before proceeding.
3. When palletizing, if damage or leakage occurs, do not proceed but rather notify the airline company and freight forwarder for handling the situation.
4. When palletizing, handle with care and strictly refrain from throwing. Where there is an upwards arrow label, place it according to the direction of the arrow and do not stack heavy objects on top.
5. When palletizing, dangerous goods shall be placed in obvious and easily accessible locations as far as possible (such as the door or outside the pallet) and secured, and not in the center, so as to facilitate the captain’s inspection and handling.
6. When palletizing, segregate the goods according to the “Dangerous Goods Storage Segregation Table” (Attachment VIII) and “Segregation Requirements for Dangerous Goods and Non-dangerous Goods” (Attachment IX) to avoid damaging the goods. For example:
A. Class 6 dangerous goods or dangerous goods with sub-hazard belonging to toxic substances shall not be palletized on the same pallet with live animals or goods with outer packaging labeled with food, feed, etc.
B. I-white, II-yellow and III-yellow radioactive material shall not be palletized on the same pallet to prevent increasing TI (transport index) and thereby expanding the radiation area.
7. After palletizing the pallet, hang the “Dangerous Goods Identification” provided by the airline company on the pallet.
(5) Transportation
1. When a pallet with dangerous goods needs to be transported to the airport, the personnel from the customs department shall transfer the pallet to the dedicated WPE109 terminal for loading dangerous goods, and re-confirm before loading:
A. Whether the “Dangerous Goods Identification” is duly completed and hung on the pallet.
B. Whether the dangerous goods are placed in an obvious location of the pallet and properly stacked and secured according to the direction.
C. Whether the outer packaging of the dangerous goods is damaged, deformed or leaked due to squeezing.
If the customs department’s personnel discover any of the above conditions, stop loading the pallet immediately, and report to the Customer Service Section and officer on duty at the Operations Section, and contact the airline company or other relevant personnel to handle the situation.
2. Pallets containing dangerous goods shall be loaded and transported separately to avoid causing adverse effects with other dangerous goods or general goods. When transporting the pallet, the driver shall also pay attention to any changes to the pallet at all times, and upon discovering any abnormal sound, smoke or odor, pull over by the side and inform the officer on duty, and contact the relevant units and personnel to handle the situation.
(6) Handling of radioactive material
If obvious damage to or leakage from the packaging of the radioactive material is found, or damage or leakage is suspected during receiving, storing, moving or palletizing, the personnel are strictly prohibited from going near the goods, and professional personnel shall be contacted to conduct radiation detection and relevant work. Necessary protective measures may be adopted where necessary, according to the regulations set by the authority concerned, to safeguard the health of people and minimize the impact.
(7) Dangerous Goods Operations Checklist
All operations of exporting dangerous goods are to be supervised and handled by the Company's specialized personnel in charge of dangerous goods. After inspecting each operation, the Dangerous Goods Operations Checklist shall be signed and filed for future reference.
(8) Filing of Dangerous Goods Export Documents
The dangerous goods warehouse administrator shall collect all documents such as “Dangerous Goods Acceptance Form”, etc., related to the dangerous goods for export stored in Farglory, and file them with the Management Section for future reference, up to a period of 18 months.
-
Dangerous goods
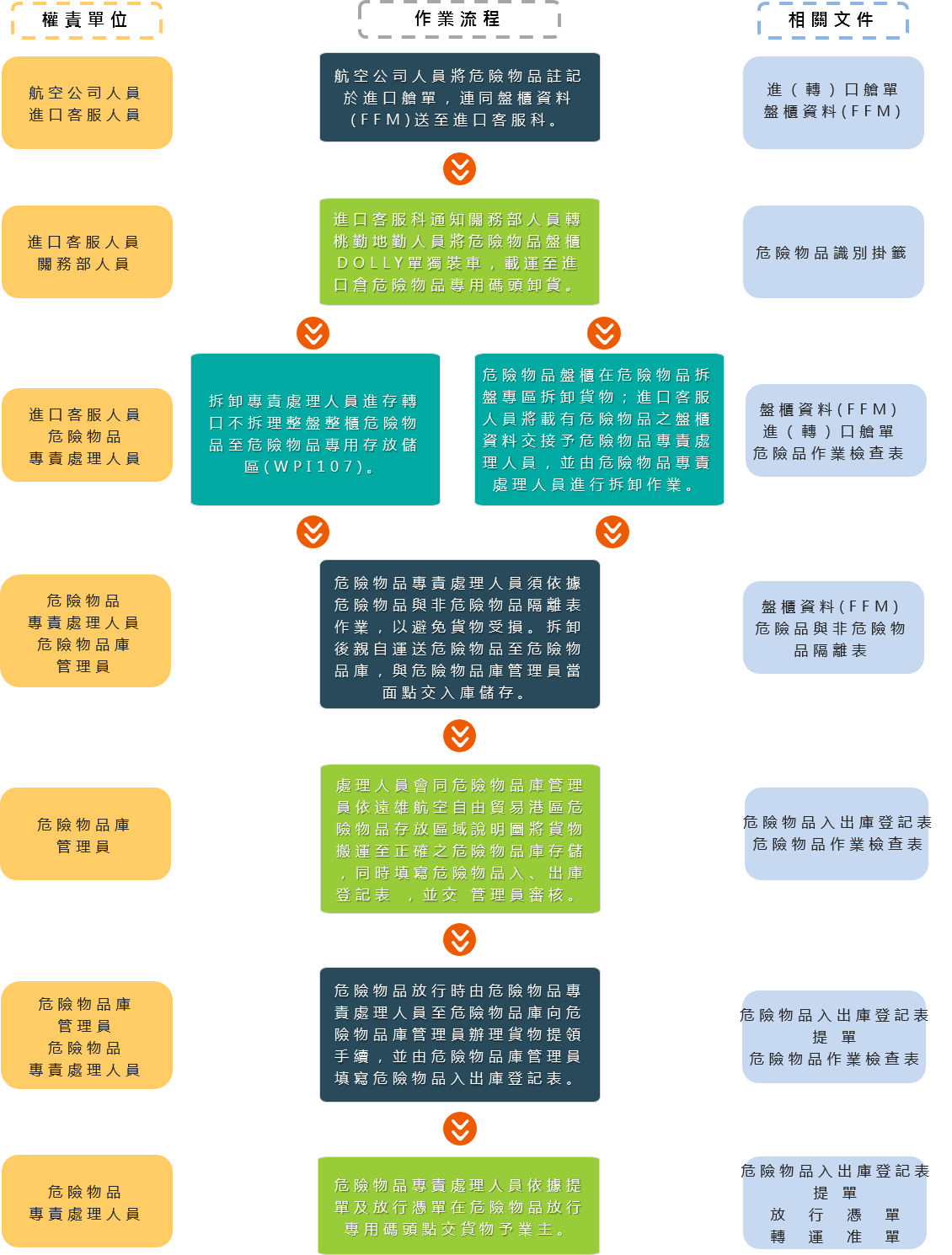
Operation Process of Import (transit) Dangerous Goods
-
Dangerous goods
Procedures for Import of Dangerous Goods
(1) Manifest acceptance operation
Airline personnel are to indicate the dangerous goods on the import manifest, and together with the Freight Forwarding Message (FFM), submit to the Import Customer Service Section.
(2) Transportation for imported dangerous goods
1. When an import pallet containing dangerous goods needs to be transported back to the import warehouse, the ground staff shall transfer the pallet to the dedicated terminal (Dangerous Goods WPI107) for unloading, and before unloading, confirm the pallet number, and verify the Dangerous Goods Identification.
2. Pallets containing dangerous goods shall be loaded and transported separately to avoid causing adverse effects with other dangerous goods or general goods. When transporting the pallet, the driver shall also pay attention to any changes to the pallet at all times, and upon discovering any abnormal sound, smoke or odor, pull over by the side and inform the officer on duty, and contact the relevant units and personnel to handle the situation.
3. When the goods arrive at the warehouse, unload the dangerous goods pallet at the dedicated terminal for unloading dangerous goods (WPI107) for the dangerous goods handling personnel to unload the goods at the dedicated area.
(3) Pallet unloading
1. Import customer service personnel are to hand the pallet information containing dangerous goods to the dangerous goods handling personnel, for the dangerous goods handling personnel to carry out the unloading.
2. The dangerous goods handling personnel shall, based on the pallet information, move the pallet to be unloaded and containing dangerous goods, to the dedicated palletizing machine (WPI101) at the dangerous goods unloading point. Transit goods will not be unloaded but moved to the special storage area.
3. Dangerous goods unloaded from the pallet shall be placed according to the “Dangerous Goods Storage Segregation Table” and “Segregation Requirements for Dangerous Goods and Non-dangerous Goods” to avoid damaging the goods. The following shall be complied during the unloading process:
A. When unloading the pallet, if damage or leakage occurs, try to place it in a temporary storage area, and contact the relevant unit according to the Dangerous Goods Accident Emergency Handling Chart and at the same time inform the airline personnel to handle the situation.
B. When unloading the pallet, handle with care and strictly refrain from throwing. Where there is an upwards arrow label, place it according to the direction of the arrow and do not stack heavy objects on top.
C. To prevent dangerous goods from falling and posing danger when transported in the warehouse, goods shall be stacked as neatly and stably as possible, with the dangerous goods label facing outwards, and the total height stacked shall not exceed 1.3 meters (including pallet thickness).
D. Class 6 dangerous goods or dangerous goods with sub-hazard belonging to a toxic substance shall not be placed in the same region as live animals or goods with outer packaging labeled with food, feed, etc.
E. I-white, II-yellow and III-yellow radioactive material shall not be stowed in the same region to prevent increasing TI (transport index) and expanding the radiation area, and thereby endangering the health of the personnel.
F. Class 4.1 and Class 5.2 dangerous goods shall be stowed in a ventilated area, and away from heat source and direct sunlight. When stowing radioactive material of II-yellow or III-yellow packaging or overpack and its content contains fissile material, the transport index of a single good cannot exceed 50 (TI<50) and the goods shall be kept at least 6 meters apart.
G. When stowing radioactive material, it shall be segregated from negatives and film. For the segregation distance, refer to IATA DGR TABLE 9.3F.
H. If suspected dangerous goods are discovered during unloading, place the goods in a temporary storage area. After notifying the airline company and receiving confirmation, store the goods in the warehouse area accordingly, and hand them over to the dedicated warehouse personnel for control and management.
(4) Goods Storage Operation
1. After completing the unloading, the dangerous goods handling personnel shall transfer the dangerous goods to the dangerous goods warehouse administrator for stowing the goods in the dedicated area according to “Farglory Free Trade Zone Dangerous Goods Storage Area Diagram”.
2. When entering the warehouse, the dangerous goods warehouse administrator shall fill in the “Dangerous Goods Entry and Exit Form”. The warehouse’s dangerous goods storage area has been designated according to the “Dangerous Goods Storage Segregation Table”. The dangerous goods warehouse administrator shall stow the goods according to the warehouse instruction tag.
3. When stowing dangerous goods with multiple hazards, its primary hazard shall be the basis of classification of storage. If the dangerous goods have sub-hazards, they must also comply with IATA DGR Table 9.3.A according to the sub-hazards, and necessary segregation measures shall be taken for incompatible dangerous goods in the warehouse storage area.
4. Dangerous goods warehouse administrators shall conduct regular patrol at every dangerous goods warehouse area on a daily basis, and ensure the goods are stowed according to the warehouse instruction tag to maintain the safety of the warehouse.
(5) Goods Picking Operations
For the picking up of dangerous goods by customers, the dangerous goods handling personnel shall provide the dangerous goods warehouse administrator at the dangerous goods warehouse with the bill of lading for picking procedures, and fill in the “Dangerous Goods Entry and Exit Form"". The dangerous goods handling personnel shall then move the dangerous goods to the import dangerous goods release area (Terminal 40) to release the goods. However, the goods shall be moved carefully and slowly, and appropriate preventive measures shall be taken to avoid causing damage.
(6) Handling of radioactive material
If obvious damage to, or leakage from, the packaging of the radioactive material is found, or damage or leakage is suspected during receiving, storing, moving or palletizing, the personnel are strictly prohibited from going near the goods, and professional personnel shall be contacted to conduct radiation detection and relevant work. Necessary protective measures may be adopted where necessary, according to the regulations set by the authority concerned, to safeguard the health of people and minimize the impact.
(7) Handling of overdue dangerous goods
1. On the 5th and 20th of each month, the information on dangerous goods stored in the warehouse for more than 35 days shall be filled out on the list of goods that have not been released by customs and submitted to the Taipei Customs Office for processing.
2. The overdue dangerous goods notified to be processed are to be transported by vehicle of professional hazardous waste disposal company delegated by Taipei Customs Office to Taipei Customs Office’s smuggled goods warehouse for storage or destruction.
3. Expired dangerous goods yet to be notified for processing are still required to be stored in the dangerous goods warehouse according to their classification, and labeled as expired dangerous goods.
(8) Import Dangerous Goods Operations Checklist
All operations of import dangerous goods are to be supervised and handled by the Company's specialized personnel in charge of dangerous goods. After inspecting each operation, the Dangerous Goods Operations Checklist shall be signed and filed for future reference.
(9) Import dangerous goods documents filing
The dangerous goods warehouse administrator shall collect all documents related to the dangerous goods for import stored in Farglory, and file them with the Management Section for future reference, up to a period of 18 months.
-
Dangerous goods
Dangerous Goods Accident Handling
In case of a dangerous goods accident, quickly evacuate the personnel, and conduct relevant emergency handling measures according to the classification based on the following table.
Please download:
Dangerous Goods Accident Handling
-
Dangerous goods
Dangerous goods related application forms download